Page 26 - Standard Indicators for the social appropriation of science
P. 26
Categories
Knowledge
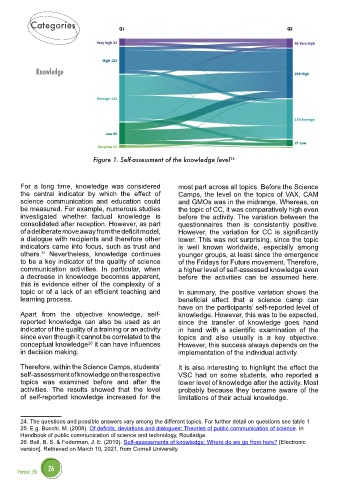
Figure 1. Self-assessment of the knowledge level 24
Figure 1. Self-assessment of the knowledge level. 24
For a long time, knowledge was considered most part across all topics. Before the Science
the central indicator by which the effect of Camps, the level on the topics of VAX, CAM
science communication and education could and GMOs was in the midrange. Whereas, on
be measured. For example, numerous studies the topic of CC, it was comparatively high even
investigated whether factual knowledge is before the activity. The variation between the
consolidated after reception. However, as part questionnaires then is consistently positive.
of a deliberate move away from the deficit model, However, the variation for CC is significantly
a dialogue with recipients and therefore other lower. This was not surprising, since the topic
indicators came into focus, such as trust and is well known worldwide, especially among
others. Nevertheless, knowledge continues younger groups, at least since the emergence
25
to be a key indicator of the quality of science of the Fridays for Future movement. Therefore,
communication activities. In particular, when a higher level of self-assessed knowledge even
a decrease in knowledge becomes apparent, before the activities can be assumed here.
this is evidence either of the complexity of a
topic or of a lack of an efficient teaching and In summary, the positive variation shows the
learning process. beneficial effect that a science camp can
have on the participants’ self-reported level of
Apart from the objective knowledge, self- knowledge. However, this was to be expected,
reported knowledge can also be used as an since the transfer of knowledge goes hand
indicator of the quality of a training or an activity in hand with a scientific examination of the
since even though it cannot be correlated to the topics and also usually is a key objective.
conceptual knowledge it can have influences However, this success always depends on the
26
in decision making. implementation of the individual activity.
Therefore, within the Science Camps, students’ It is also interesting to highlight the effect the
self-assessment of knowledge on the respective VSC had on some students, who reported a
topics was examined before and after the lower level of knowledge after the activity. Most
activities. The results showed that the level probably because they became aware of the
of self-reported knowledge increased for the limitations of their actual knowledge.
24. The questions and possible answers vary among the different topics. For further detail on questions see table 1
25. E.g. Bucchi, M. (2008). Of deficits, deviations and dialogues: Theories of public communication of science. In
Handbook of public communication of science and technology, Routledge.
26. Bell, B. S. & Federman, J. E. (2010). Self-assessments of knowledge: Where do we go from here? [Electronic
version]. Retrieved on March 10, 2021, from Cornell University
26
Persist_EU